Responsible Use of Biometrics in Digital Identity
21/1/25, 10:00 am
Introduction
Digital identity—the collection of electronic information that represents individuals, organisations, or devices—has become essential in verifying and securing access to digital services. Biometrics, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and voiceprints, provide a highly secure method of authentication, enabling robust verification and fostering user trust. However, responsible implementation is critical to address privacy and security concerns while maximising utility.
Core Functions of Digital Identity
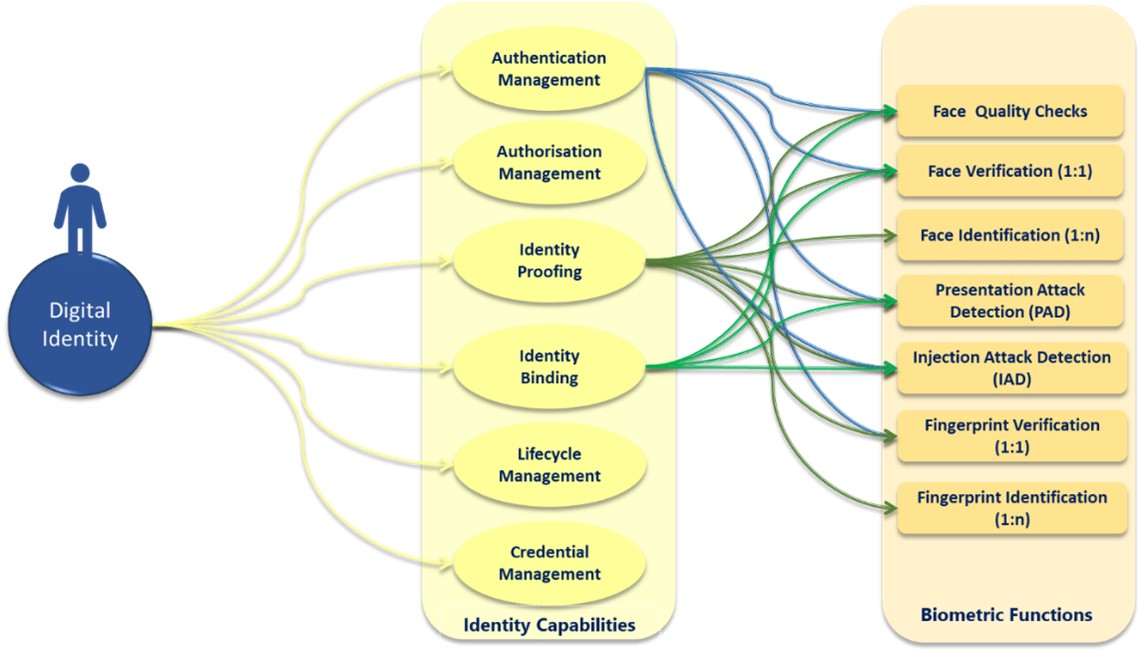
Authentication Management
Biometrics enhance authentication by ensuring that only authorised individuals access services. Techniques like face verification and liveness detection prevent fraudulent actions, such as spoofing and injection attacks, improving both security and user experience.
Identity Proofing
Identity proofing verifies individuals by validating their biographic and biometric data against trusted sources. Once verified, biometric templates are securely stored, creating a reliable foundation for future interactions. Features like presentation attack detection ensure the uniqueness and authenticity of identities.
Identity Binding
Identity binding links verified identities to digital or physical credentials. Biometric data secures this connection through functions such as face verification, ensuring that credentials remain unique and tamper-proof.
Emerging Trends in Responsible Biometrics
Biometrics will be instrumental in shaping the future of identity solutions, including decentralized identity systems and the digital integration of physical identity cards. By enhancing security, safeguarding privacy, and fostering user confidence, biometrics will drive the evolution of next generation identity solutions.
Decentralised Identity Credentials
Decentralised identity credentials, such as verifiable credentials and mobile driver’s licenses, are rapidly gaining traction. These credentials can be issued directly to a holder's app or digital wallet, installed on the person’s mobile device. Both verifiable credentials and mobile driver’s licenses include face biometric data as one of their key attributes.
To ensure security, these credentials must be linked to the holder app through biometrics, such as their face. When a user shares their credentials with digital services, the face biometric data within the credential should be verified against the user’s live face. The holder app must utilise advanced biometric techniques, such as face verification, presentation attack detection, and injection attack detection, to ensure that the credentials are being shared by their rightful owner. By leveraging “Biometrics as a Service” (BaaS), biometrics providers can deliver tailored solutions for digital credential issuers, holder app providers and users.
QR-Enabled Physical Identity Cards
For underserved populations and environments with limited digital access, QR-enabled physical ID cards bridge traditional and digital systems. These cards embed biometric data within QR codes, offering seamless and secure identity verification. Compliance with global standards, such as ISO/IEC 18013-5 (mDL/mdoc), ensures security and interoperability.
The data in mdoc is typically encoded as CBOR (Concise Binary Object Representation) tokens, chosen for their compactness and efficiency. CBOR tokens are structured data objects encoded in a lightweight format, making them ideal for use in constrained environments where size and processing efficiency are critical, offering an advantage. Since CBOR tokens are lightweight, they are well-suited for generating QR codes on physical identity cards. The CBOR token encapsulates identity data, a biometric template, and the issuer's digital signature, secured with advanced signing methods. This ensures data integrity and facilitates trusted interactions.
Users can use their QR enabled physical identity card to access digital services. By incorporating biometric verification, digital service can match the facial data stored in the QR code on the card with the individual attempting to use the application service, ensuring secure and reliable access. By leveraging “Biometrics as a Service” (BaaS), biometrics providers can deliver tailored solutions for digital service providers, physical identity card issuers and users.

Ethical and Security Considerations
As reliance on biometrics grows, addressing ethical and security challenges is vital to maintain user trust. Key measures include:
Explicit User Consent
Ensure transparency by obtaining informed consent before collecting biometric data.
Encryption
Always protect data, whether in transit or storage, using robust encryption techniques.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly update systems to counter evolving threats, such as deepfakes and spoofing.
Biometric Reset
Enable periodic updates to biometric templates to enhance security and mitigate risks.
Auditing and Monitoring
Implement consistent audits to detect and address unauthorised access or misuse.
User-Centred Design
Prioritise usability to encourage adoption, testing solutions with real users and incorporating their feedback.
Unbiased Biometrics
Regular audits and testing should ensure equitable performance regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity.
Policy Frameworks
Develop comprehensive guidelines for data collection, storage, and disposal to ensure accountability and compliance.
Practical Applications & Case Studies
Decentralised Identity in Action
A national e-passport programme demonstrates the potential of decentralised identity systems. By incorporating facial biometrics and on-device verification, the programme enabled secure, contactless border control, reducing wait times while safeguarding privacy.
QR-Enabled ID for Healthcare Access
In healthcare initiatives where mobile phone use is not possible, QR-enabled ID cards facilitated seamless patient identification and access to medical records. Biometrics ensured the authenticity of user identities, enhancing service delivery while maintaining data security.
QR-Enabled Student ID for Social Media Ban
Schools are seeking limit mobile phone usage to effectively support and enforce a social media ban. Schools can issue QR-enabled ID cards to students which provides a convenient and efficient way to verify student identities and grant access to essential digital services without requiring mobile devices. Biometrics ensured the authenticity of student identities, enhancing service delivery while maintaining data security.
Conclusion
Biometrics are transforming digital identity, offering enhanced security, accessibility, and convenience. However, their potential can only be realised through responsible implementation.
By prioritising ethics, transparency, and user trust, the industry can create systems that are secure, inclusive, and aligned with societal expectations.
Collaboration across sectors is essential to shape a future where biometrics are not only effective but also equitable and trusted.

Venkat Maddali
Principal Architect - Biometrics
venkat.maddali@nec.com.au




